October 15, 2014
For this experiment a system with two batteries in series and two light bulbs in parallel were used and the volt was measure, and the amp was measure in three different places. Also two batteries in parallel and two light bulbs in series were used. The same measurements were done for this system.
3 different resistors were given and we were asked to find out how much they can handle. There are 4 strips on the resistors 3 colors, each color represent a number from 0 to 9, and 1 strip, either silver or gold, which determines the error from the actual value. Then the actual values were measured usin a multi-meter.
These calculations show the calculations to show the total amount of resistance of the resistor in series and in parallel.
This shows the resistors being calculated from the previous picture.
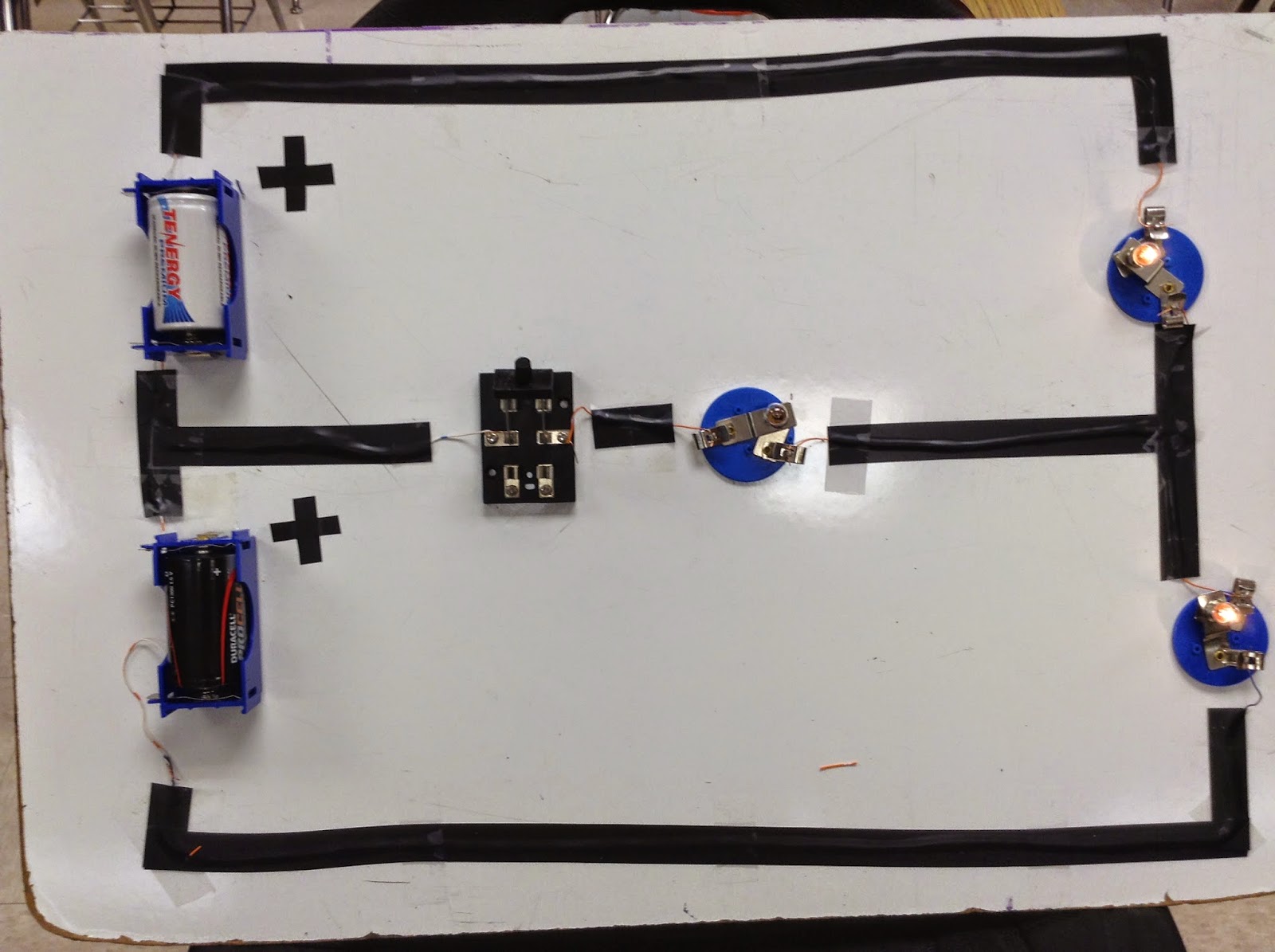
Before the middle switch was closed, both the outer light were brightly lit. Then the middle switch was closed, the middle light bulb did not turn open.
This is a more detailed explanation for how the system works.
The two batteries on the left are used to light up both the light bulb. Then when the switch is closed and a battery is introduced in the system. The additional battery did not affect the system.
This picture explains the previous picture during class.